Distributed Dictionary Performance
How well does the DDict perform? We improve Dragon performance with each release, but
this is where we are at with Dragon v0.12.1. For the gups_ddict.py , inspired by the classic
GUPS (Global Updates Per Second) benchmark, some
large number of processes will
put or get a unique set of key/value pairs into or from the DDict. The keys are always 128 bytes
in size in this implementation, but the values vary in length. Figure Fig. 39 below shows the aggregate
bandwidth measured across the clients for writing key/value pairs into a DDict sharded across
up to 512 nodes on a Cray EX system. For the largest value sizes, DDict is achieving ~1/3 of
the hardware-limited network bandwidth and scales linearly with the number of nodes.
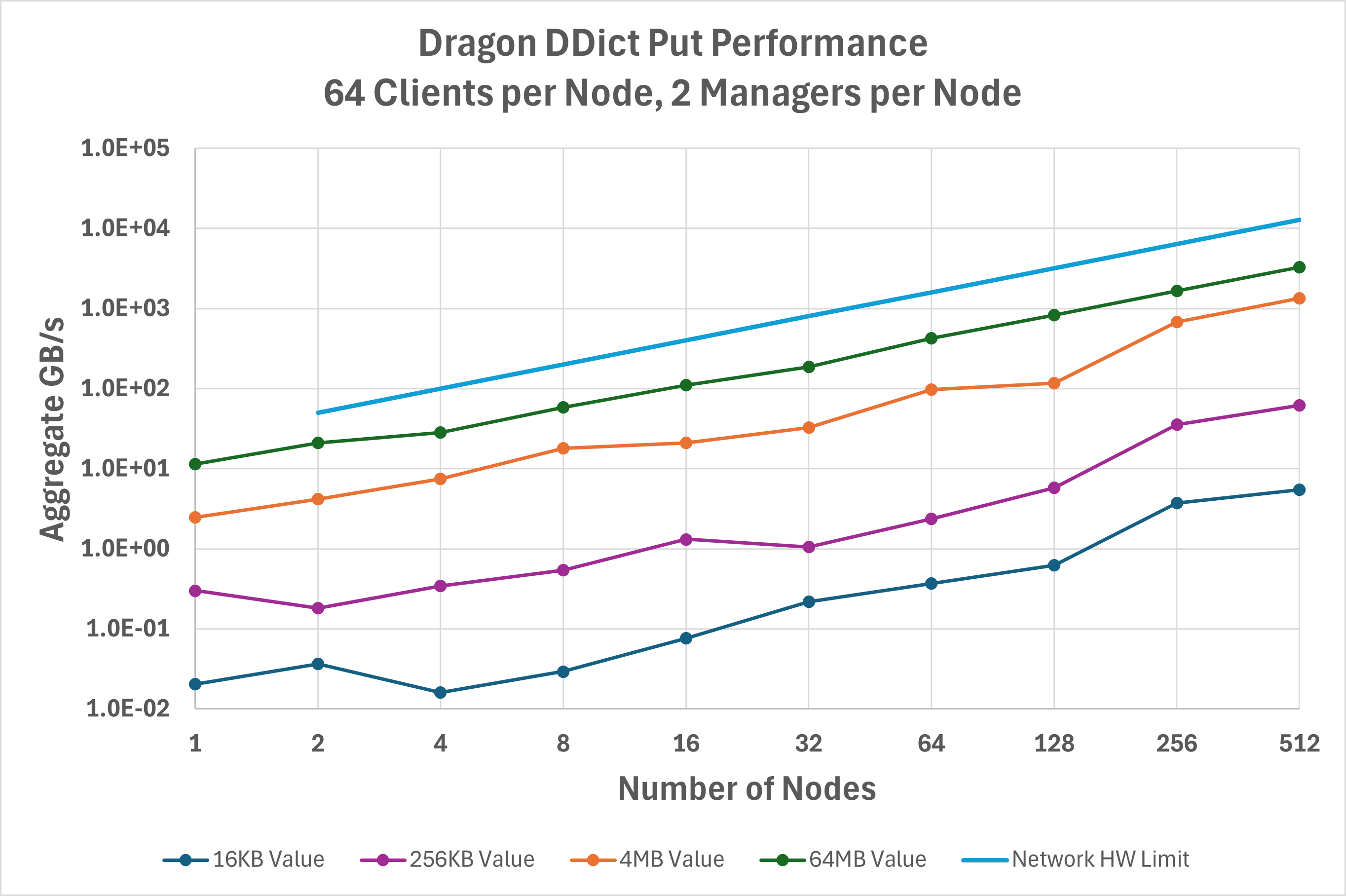
Fig. 39 Aggregate bandwidth for the put operation on a DDict.
Figure Fig. 40 shows similar data but now using start_batch_put() and
end_batch_put() to enable aggregating operations, which can eliminate some overhead in
communicating with managers. In comparison with basic put() operations, this optimization
is most effective at lower client node counts and values less than 1 MB. For example, 4 KB values on a single node
achieve 5.6X higher throughput using batched operations. At large node counts, however, batched operations may reduce
performance.
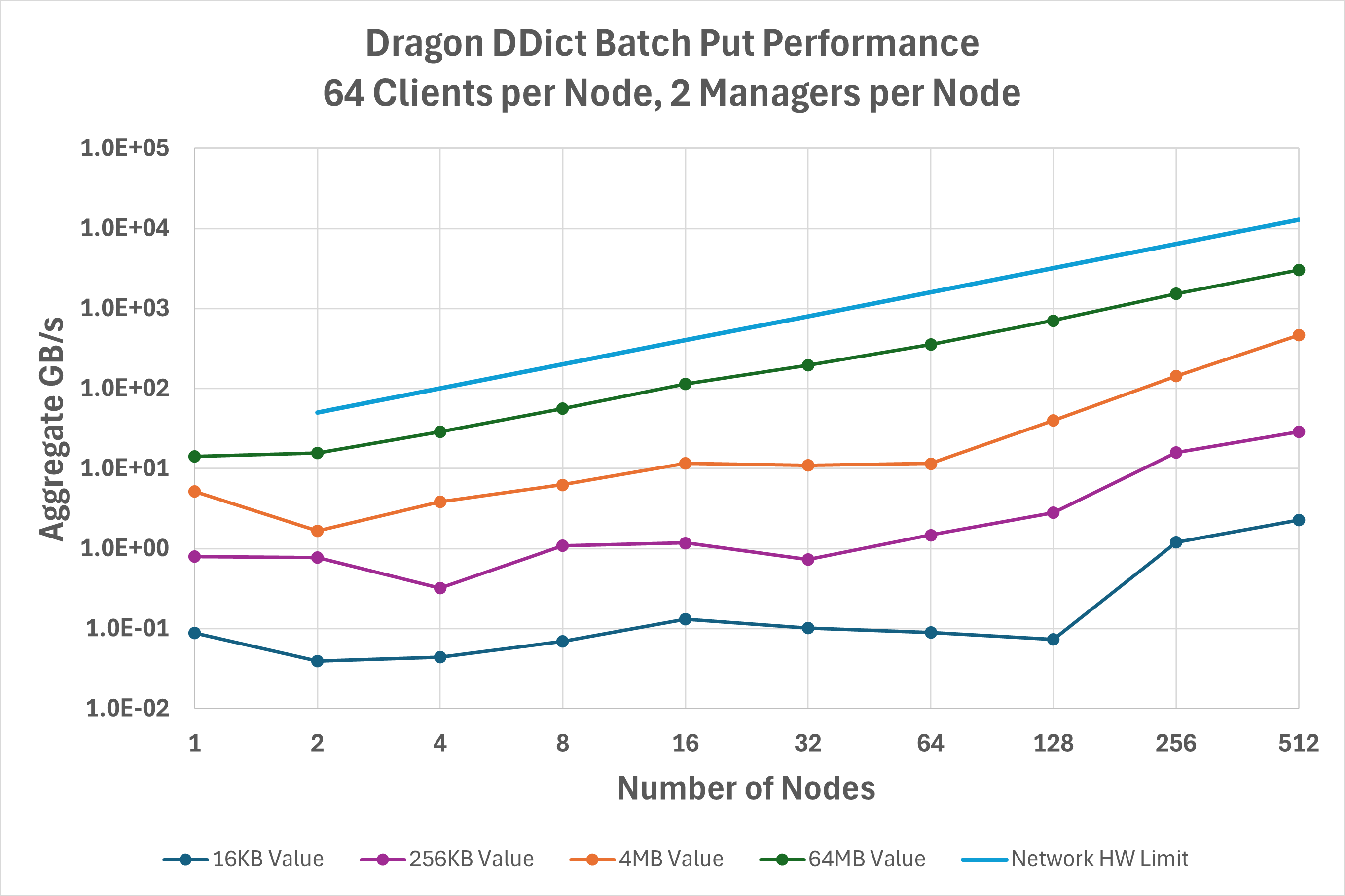
Fig. 40 Aggregate bandwidth for the batched put operation on a DDict.
Figure Fig. 41 is the same but now for get() operations. Additional
optimizations were recently done to this path for read-heavy use cases, such as AI training data loading, that account
for get() frequently achieving higher performance than put()
in the v0.12.1 release.
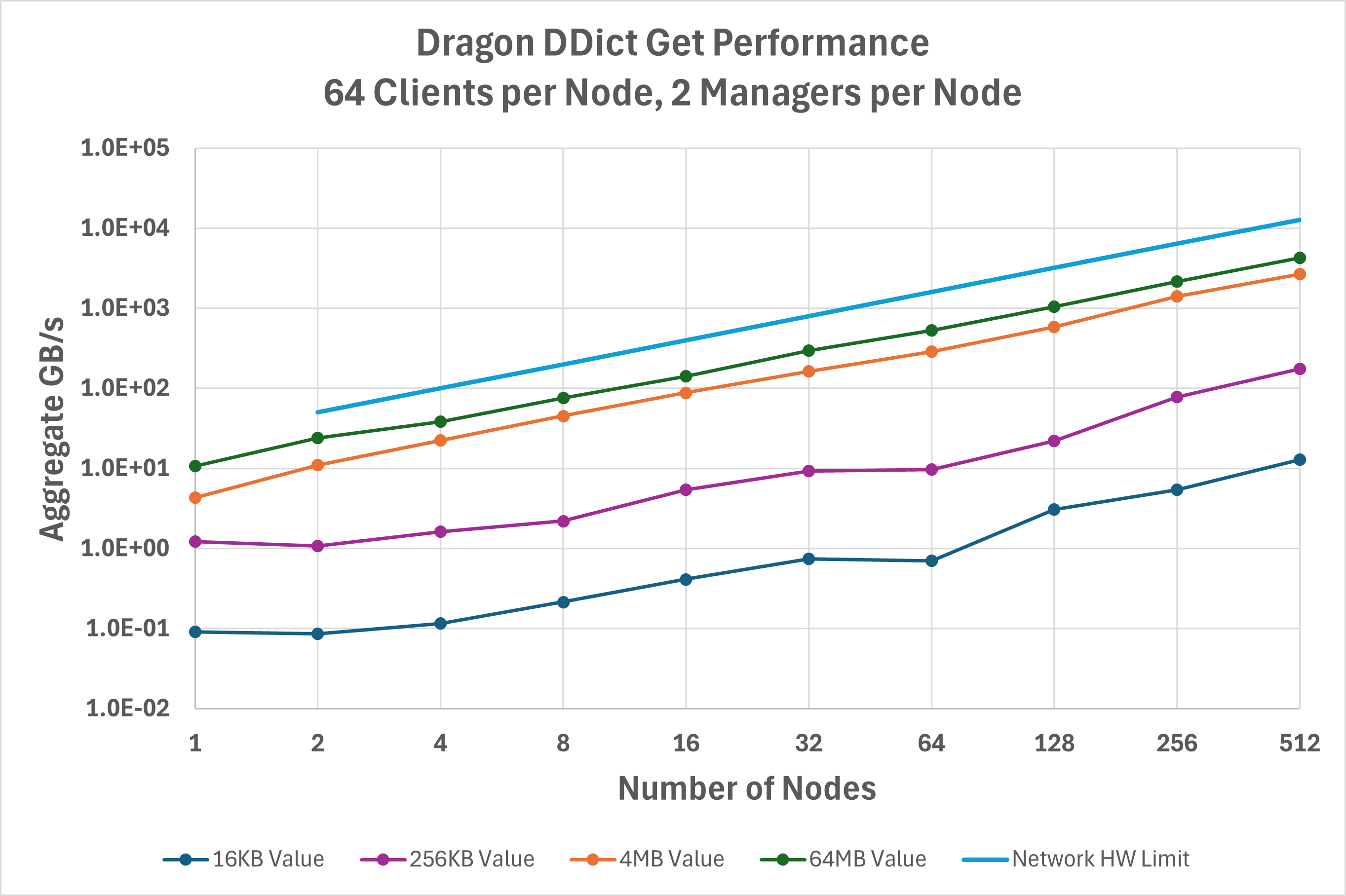
Fig. 41 Aggregate bandwidth for the get operation on a DDict.
A new feature added in v0.12 is the ability to freeze() a DDict.
A frozen DDict allows clients more direct access to dictionary buffers and eliminates some
required copy overheads. This optimization is most effective at low client node counts and large value sizes,
as seen in Figure Fig. 42. For example, 64 MB values on a single node achieve 2X higher read
throughput with a frozen DDict, and 16 MB values on two nodes achieve 1.5X higher throughput.
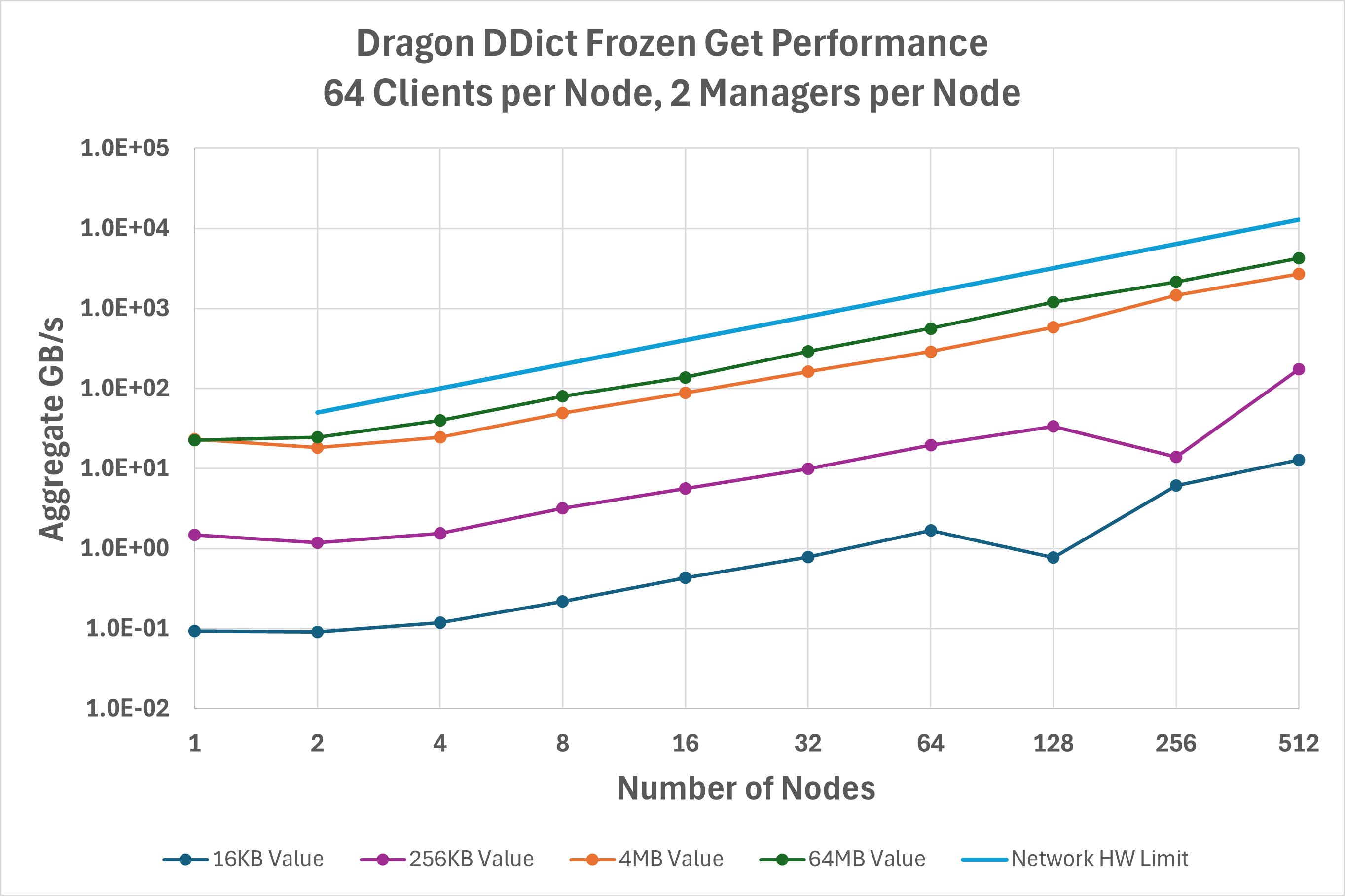
Fig. 42 Aggregate bandwidth for the get operation on frozen a DDict.
All data was gathered on a Cray EX system equipped with a single HPE Slingshot 200Gbps NIC on each node. To run the same benchmarks:
export DRAGON_DEFAULT_SEG_SZ=21474836480
dragon gups_ddict.py --benchit